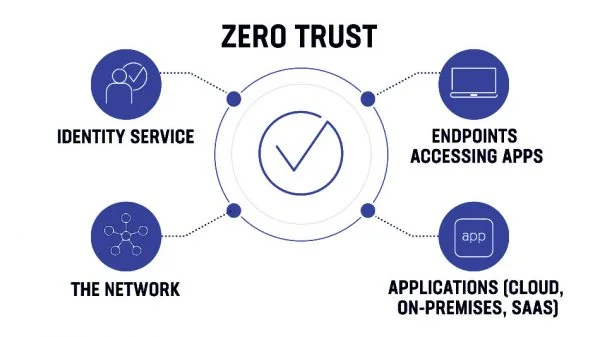
Zero Trust is a modern cybersecurity framework designed to protect digital systems in an era of constant cyber threats. Unlike traditional security models that assume trust within a network, Zero Trust operates on a simple principle: never trust, always verify.
As organizations adopt cloud services, remote work, and mobile devices, network boundaries have become less defined. Zero Trust addresses these challenges by enforcing strict identity verification and access controls at every level.
What Is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a security model that requires continuous authentication and authorization for every user, device, and application attempting to access resources. Trust is never assumed, even if the request comes from inside the network.
This approach minimizes the risk of insider threats, stolen credentials, and lateral movement by attackers. Every access request is evaluated based on identity, device health, location, and behavior.
Core Principles of Zero Trust
Zero Trust is built on several foundational principles that strengthen security:
Verify Explicitly
All users and devices must be authenticated before gaining access, using methods such as multi-factor authentication.
Least Privilege Access
Users are granted only the minimum access necessary to perform their tasks.
Assume Breach
The model assumes attackers may already be inside the network and limits their ability to move freely.
These principles help reduce attack surfaces and improve overall resilience.
How Zero Trust Works
Zero Trust works by continuously monitoring and validating access requests. Instead of relying on perimeter-based defenses, it uses identity-based controls and real-time risk assessments.
When a user attempts to access a system, Zero Trust evaluates multiple signals, including login credentials, device security status, and user behavior. Access is granted only if all conditions meet security policies.
Understanding 👉 Identity-Centric Access Control Architecture 👈 provides deeper insight into how Zero Trust enforces secure access across modern IT environments.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust offers several advantages for organizations:
- Reduces the risk of data breaches
- Protects remote and hybrid work environments
- Improves visibility into user and device activity
- Limits damage caused by compromised accounts
By continuously verifying access, Zero Trust significantly enhances security posture.
Zero Trust vs Traditional Security Models
Traditional security models focus on protecting the network perimeter. Once users are inside, they are often trusted by default. This approach is no longer effective against modern threats.
Zero Trust removes implicit trust and applies security controls everywhere. It protects users, data, and applications regardless of location, making it ideal for cloud-first and remote organizations.
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
While Zero Trust is highly effective, implementation can be challenging. Organizations may face issues such as:
- Integrating legacy systems
- Managing identity and access policies
- Ensuring user convenience without sacrificing security
A phased implementation approach helps overcome these challenges while maintaining productivity.
Future of Zero Trust
The future of Zero Trust is closely tied to cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and automation. As cyber threats become more advanced, Zero Trust frameworks will rely on machine learning to detect anomalies and respond instantly.
Zero Trust is expected to become a standard security approach across industries such as finance, healthcare, and government. Organizations that adopt it early gain a strong defensive advantage.
Conclusion
Zero Trust represents a shift in how cybersecurity is approached in modern digital environments. By eliminating implicit trust and continuously verifying access, Zero Trust helps organizations defend against evolving cyber threats. As digital transformation accelerates, Zero Trust will remain a cornerstone of effective cybersecurity strategies.