Malware and firewall solutions are two essential pillars of modern cybersecurity. As digital systems become more connected, the risk of cyber threats increases significantly. Malware attacks can damage systems, steal sensitive data, and disrupt operations, while firewalls act as a protective barrier that controls network traffic.
Together, malware protection and firewalls form a strong defense mechanism that helps organizations and individuals secure their digital environments from cybercriminals.
What Is Malware?
Malware, short for malicious software, refers to any program designed to harm, exploit, or gain unauthorized access to systems. Malware can infect computers, servers, mobile devices, and networks without the user’s knowledge.
Common types of malware include:
- Viruses: Attach themselves to files and spread when executed
- Worms: Self-replicate and spread across networks
- Trojans: Disguised as legitimate software
- Ransomware: Encrypts data and demands payment
- Spyware: Collects user data secretly
Malware attacks can lead to financial loss, data breaches, and system downtime.
How Malware Infects Systems
Malware commonly spreads through phishing emails, malicious websites, infected downloads, and unsecured networks. Once inside a system, it can run silently in the background and compromise security.
Poor security practices, outdated software, and weak passwords make systems more vulnerable to malware infections.
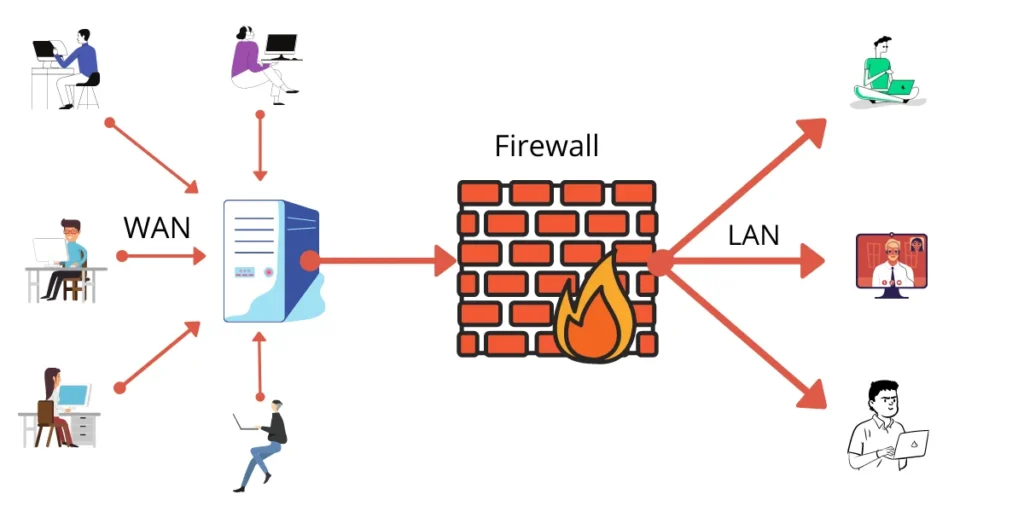
What Is a Firewall?
A firewall is a security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules. It acts as a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, such as the internet.
Firewalls can be hardware-based, software-based, or cloud-based. Their main purpose is to prevent unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication to pass through safely.
Types of Firewalls
Different types of firewalls are used depending on security needs:
Packet-Filtering Firewalls
Inspect data packets and block traffic based on rules.
Stateful Inspection Firewalls
Track active connections and make smarter filtering decisions.
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW)
Offer advanced features like intrusion prevention and application awareness.
Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
Protect web applications from attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
Each type adds an extra layer of defense against cyber threats.
How Malware and Firewalls Work Together
Malware and firewall solutions complement each other in cybersecurity strategies. While firewalls block unauthorized network access, malware protection tools detect and remove malicious software that enters a system.
Firewalls reduce exposure to threats, and anti-malware tools handle infections that bypass defenses. Learning more about 👉 Threat Mitigation Through Layered Security Models 👈 helps explain why combining multiple defenses is essential in modern cybersecurity.
Importance of Malware and Firewall Protection
Using malware and firewall protection is critical for several reasons:
- Prevents unauthorized system access
- Protects sensitive personal and business data
- Reduces the risk of financial loss
- Maintains system performance and uptime
Without these protections, systems are highly exposed to cyberattacks.
Best Practices for Malware and Firewall Security
To strengthen security, organizations should follow best practices such as:
- Keeping software and operating systems updated
- Using reputable antivirus and anti-malware tools
- Configuring firewall rules correctly
- Regularly monitoring network activity
- Training users on cybersecurity awareness
These practices significantly lower the risk of cyber threats.
Future of Malware and Firewall Technologies
As cyberattacks grow more sophisticated, malware and firewall technologies are evolving rapidly. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are now being integrated to detect threats in real time.
Future firewalls will become more adaptive, while malware detection systems will focus on behavior-based analysis rather than signature-based methods. This evolution will help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats.
Conclusion
Malware and firewall technologies are fundamental to protecting digital systems in today’s connected world. Malware poses serious risks, while firewalls provide a critical defense layer against unauthorized access. By combining both solutions and following best practices, organizations can build a strong cybersecurity posture and safeguard their digital assets effectively.